NCERT Solutions Class 7 Social Science Geography Air (along with questions and answers and notes). The earth is covered by a huge blanket of air that is known as the ‘atmosphere.’ In this chapter, we will learn about the components of the atmosphere and the geographical changes that it undergoes from time to time.
Read more: NCERT Solutions for Class 7 Social Science Geography Chapter 6: Natural Vegetation and Wildlife
Table of Contents
Summary – NCERT Solutions Class 7 Social Science Geography Air
Composition of the Atmosphere
- Nitrogen and oxygen are the two gases which make up the bulk of the atmosphere while Carbon dioxide, helium, ozone, argon and hydrogen are found in lesser quantities.
- Apart from these gases, tiny dust particles are also present in the air.
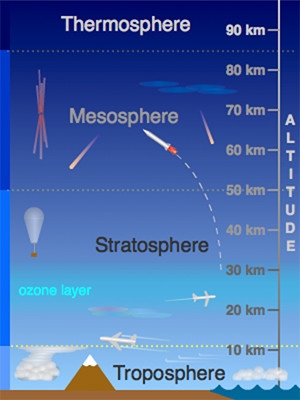
Temperature
- The temperature is considered the degree of warmth and coldness of the air.
- Insolation is an significant factor that affects the distribution of temperature, not just between day and night, but also from season to season. Insolation is the incoming solar power that the earth intercepts.
- From the equator towards the poles, the level of insolation reduces.
- Temperature is measured in Celsius and Fahrenheit.
Air pressure
- Air pressure is defined as the pressure exerted on the earth’s surface by the weight of air.
- The distribution of air pressure is horizontally determined by the air temperature at a given location.
- The climate is cool in regions which have a lower temperature this is because the weather often travels from regions of high pressure to areas of low pressure.
Wind
- The movement of air from high-pressure areas to the low-pressure area is called Wind.
- Winds can be broadly divided into three types: permanent winds, seasonal winds and local winds.
- On 25 October 1999, cyclonic winds originated as depression and affected Odisha killing thousands of people.
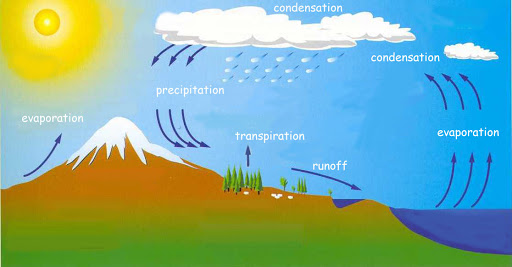
Moisture
- There are three types of rainfall: the convectional rainfall, the orographic rainfall and the cyclonic rainfall and it is very important for the survival of plants and animals.
Conclusion – NCERT Solutions Class 7 Social Science Geography Air
NCERT Solutions Class 7 Social Science Geography Air (along with questions and answers and notes as given above). The atmosphere is a thin blanket of air that surrounds the earth. It protects us from the harmful rays of the sun. It consists of the main nitrogen (78%) and oxygen (21%). Carbon dioxide, helium, ozone, argon and hydrogen are found in lesser quantities.
Questions and Answers – NCERT Solutions Class 7 Social Science Geography Air
1. Answer the following questions.
(i) What is the atmosphere?
Answer: The blanket of air surrounding the earth is called the atmosphere. The atmosphere primarily comprises nitrogen and oxygen in bulk and other gases like carbon dioxide, helium, ozone, etc in lesser quantities. All living beings on earth depend on the atmosphere for their survival.
(ii) Which two gases make the bulk of the atmosphere?
Answer: The two gases that make the bulk of the atmosphere are:
- Oxygen (21%)
- Nitrogen (78%)
(iii) Which gas creates a greenhouse effect in the atmosphere?
Answer: Carbon dioxide is the gas that creates the greenhouse effect in the atmosphere.
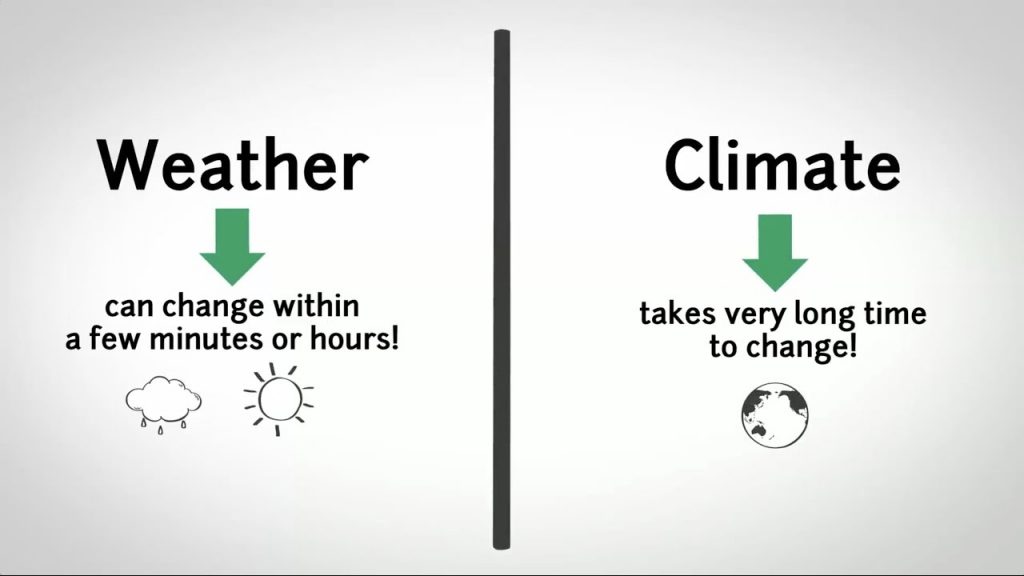
(iv) What is the weather?
Answer: The hour to hour or the day to day condition of the atmosphere is called weather. Weather can change dramatically from day-to-day. It may be classified as hot, dry, cold or wet.
(v) Name three types of rainfall?
Answer: The three types of rainfall are as follows:
- Convectional rainfall
- Orographic rainfall
- Cyclonic rainfall
(vi) What is air pressure?
Answer: Air pressure is defined as the pressure exerted by the weight of air on the earth’s surface. The air pressure decreases as height increases and is the highest at the sea level.
2. Tick the correct answer.
(i) Which of the following gases protects us from harmful sun rays?
(a) Carbon dioxide
(b) Nitrogen
(c) Ozone
Answer: c
(ii) The most important layer of the atmosphere is
(a) Troposphere
(b) Thermosphere
(c) Mesosphere
Answer: a
(iii) Which of the following layers of the atmosphere is free from clouds?
(a) Troposphere
(b) Stratosphere
(c) Mesosphere
Answer: b
(iv) As we go up the layers of the atmosphere, the pressure
(a) Increases
(b) Decreases
(c) Remains the same
Answer: b
(v) When precipitation comes down to the earth in the liquid form, it is called
(a) Cloud
(b) Rain
(c) Snow
Answer: b
3. Match the following.
| (i) Trade Winds | (a) Incoming solar energy |
| (ii) Loo | (b) Seasonal wind |
| (iii) Monsoon | (c) The horizontal movement of Air |
| (iv) Wind | (d) A layer of ozone gas |
| (e) Permanent wind | |
| (f) Local wind |
Answer:
| (i) Trade Winds | (e) Permanent wind |
| (ii) Loo | (f) Local wind |
| (iii) Monsoon | (b) Seasonal wind |
| (iv) Wind | (c) The horizontal movement of Air |
4. Give reasons.
(i) Wet clothes take longer time to dry on a humid day?
Answer: Wet clothes take longer time to dry on a humid day because the amount of water in the air is more on a humid day than on a sunny day. Due to which, the rate of evaporation decreases and air soaks in less water from the clothes.
(ii) Amount of insolation decreases from the equator towards poles?
Answer: Insolation is the incoming solar energy intercepted by the earth. The amount of insolation decreases from the equator toward the poles, because sun rays fall vertically on the equator and slant on the poles.





