Table of Contents
Class 7 Science NCERT solution Chapter 1 Summary
All living organisms, be it plants or animals, need energy that will help them in carrying out their day to day activities. The energy is generated from the food they consume. The process by which the living creatures consume food and convert them into energy is called nutrition. Nutrition plays an important role in a living creature’s life.
Read more: NCERT Solutions For Class 7 Science Chapter 10 Respiration in Organisms
Nutrition helps in giving energy plus other vital elements that will help the organism sustain and live life healthily and happily. The food consumed to obtain nutrition is composed of components known as nutrients.
These include carbohydrates, proteins, fats, vitamins and minerals. These nutrients are very important as they help the living organism to grow, build their bodies and repair damaged parts of their bodies. Nutrition in plants is mainly of three types:
- Autotrophic Nutrition
- Heterotrophic Nutrition
- Saprotrophic Nutrition
AUTOTROPHIC NUTRITION
It is a kind of nutrition in which the living organisms are able to make their food themselves by the use of simple substances. It is derived from two words, namely ‘auto’ meaning self and ‘trophos’, meaning nourishment.
As it effectively translates into self-nourishment, it is most often found in plants. They are called autotrophs. The plants make their own food by a unique and industrious process known as photosynthesis.
Photosynthesis in Plants:
The process of synthesis or preparation of food by plants by combining sunlight, carbon dioxide from the air and water from earth to create starch and release oxygen is known as photosynthesis.
It is derived from two words, ‘photo’ which means light and ‘synthesis’ meaning ‘to combine’.
During photosynthesis, chlorophyll containing cells of leaves, in the presence of sunlight, use carbon dioxide and water to synthesise carbohydrates (glucose).

Process of Photosynthesis:
a. It occurs in the leaves of the plants, which are known as factories of food production.
b. Water and minerals are absorbed from the earth from the roots and transported to the leaves through vessels that run as pipes through the roots, branches, stems and leaves.
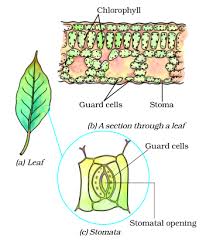
c. Carbon dioxide is taken from the air through the stomata (small pores) present on the surface of the leaves.
d. Chlorophyll: These are green pigments present in the leaves that help to catch the energy from the sunlight. This energy is then used to combine all the components and prepare the food.
e. Thus, solar energy captured by the leaves and stored in the form of food in the plant.
Characteristics of photosynthesis
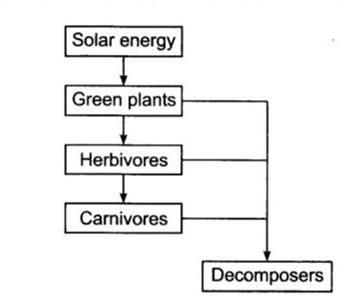
a. Photosynthesis is the main source of food for all living organisms as they are directly and indirectly dependent on plants to source their food.
b. Photosynthesis releases oxygen which is the primary necessity for survival of living organisms on earth.
c. It generates carbohydrates that are used by plants to make further nutrients required for their survival.
d. It takes place on the green stems and branches too. For example, this can be seen in the desert plants who have spine like leaves to reduce water loss by transpiration.
e. Leaves that are not green in color also have chlorophyll that they use for photosynthesis. Other pigments of red or brown color mask the green color.
Important Terms associated with Photosynthesis
Cells: They are tiny units that make the bodies of living organisms. They are made of a centrally located spherical structures known as nucleus, surrounded by a jelly like substance called cytoplasm and covered by a thin outside boundary known as cell membrane.
Stomata: They are tiny pores present on the surface of the leaves that help in the exchange of oxygen and carbon dioxide. They are surrounded by guard cells.
Synthesis of other nutrients in plants
Apart from carbohydrates, plants also have other components such as proteins and fats in them. They use the carbon, hydrogen and oxygen from the carbohydrates along with nitrogen to make them.
Bacteria present in the soil convert the nitrogen present in air into a usable form and releases it into the soil. This is then absorbed by plants through water and further used to synthesize proteins and vitamins needed by them.
HETEROTROPHIC NUTRITION
Generally, animals and almost all other organisms that take their food from plants are known as heterotrophs. Certain plants that do not have chlorophyll, also depend on food produced by other plants. Such kind of nutrition is known as heterotrophic nutrition.
Parasitic Plants: Amarbel (Cuscuta) derives its nutrients by climbing on another plant. The plant providing the nutrients is known as the host and Cuscuta as the parasite. Such kinds of plants are known as parasitic plants.
Insectivorous Plants:
Plants that eat insects are known as insectivorous plants. For example, Pitcher plant has modified its leaves to create a jug like structure with a lid that can open and close to trap insects.
Once trapped, the insect gets digested by the digestive juices secreted into the jug and the nutrients are absorbed by the plant. Insectivorous plants are partial heterotrophs.
SAPROTROPHIC NUTRITION
The mode of nutrition in which organisms take in nutrients from dead and decaying matter is called saprotrophic nutrition. Such organisms with saprotrophic mode of nutrition are called saprotrophs. For example, mushrooms and moulds.
Fungi: They generally grow on substances kept in hot and humid weather. Particularly during the rainy season, fungal spores are generally present in the air. When they land on wet and warm things they germinate and grow.
Symbiosis
It a process by which some organisms live together and share both shelter and nutrients. For example, certain fungi live inside the roots of plants. The plants provide nutrients to the fungus and, in return, the fungus provides water and certain nutrients.
Lichens: They are organisms in which two organisms live together; a chlorophyll contain alga and a fungus. The fungus provides shelter, water and minerals to the alga and, in return, the alga prepares and provides food to the fungus.
Rhizobium: It is a bacterium that helps in replenishing the depleted nitrogen content in the soil once used up by the plants to create their nutrients. Rhizobium can take atmospheric nitrogen and convert it into a usable form in the soil.
But since Rhizobium cannot make its own food, it often lives in a symbiotic relationship in the roots of gram, peas, moong, beans and other legumes and provides them with nitrogen. In return, the plants provide it food and shelter.
This association is of great significance for the farmers. They can reduce the use of nitrogenous fertiliser where leguminous plants are grown and save the environment.
EXERCISE
Q1. Why do organisms take food?
A1. All living organisms need energy that will help them in carrying out their day to day activities. The energy is generated from the food they consume. The food consumed is composed of components known as nutrients. These nutrients, and thus food are very important as they help the living organism to grow, build their bodies and repair damaged parts of their bodies.
Q2. Distinguish between a parasite and a saprotroph.
A2. Solution:
| Saprophytes | Parasites |
| Acquire nutrients from dead and decaying matter | Parasites live on or in a host and get its food at the expense of its host |
| E.g.: Fungi | E.g.: Cuscuta |
Q3. How would you test the presence of starch in leaves?
A3. Take two potted plants of the same kind. Keep one in the dark for 72 hours and the other in sunlight. Perform the iodine test with the leaves of both the plants. Now leave the pot which was earlier kept in the dark, undisturbed for 3 – 4 days in sunlight and perform the iodine test again on its leaves.
Iodine test: Put iodine solution on the leaf
Observation: Blue-black colour will be observed on the leaves of the plant kept in sunlight, which indicates the presence of starch. It will not be observed on the leaves of plant kept in the darkroom. This indicates the absence of starch.
Q4. Give a brief description of the process of synthesis of food in green plants.
A4. The process of synthesis or preparation of food by plants by combining sunlight, carbon dioxide from the air and water from earth to create starch and release oxygen is known as photosynthesis.
Process of Photosynthesis:
It occurs in the leaves of the plants, which are known as factories of food production.
Water and minerals are absorbed from the earth from the roots and transported to the leaves through vessels that run as pipes through the roots, branches, stems and leaves.
Carbon dioxide is taken from the air through the stomata (small pores) present on the surface of the leaves.
Chlorophyll: These are green pigments present in the leaves that help to catch the energy from the sunlight. This energy is then used to combine all the components and prepare the food.
Thus, solar energy captured by the leaves and stored in the form of food in the plant.
Equation:

Q5. Show with the help of a sketch that plants are the ultimate source of food.
Q6. Fill in the blanks:
(a) Green plants are called autotrophs since they synthesise their food.
(b) The food synthesised by plants is stored as starch.
(c) In photosynthesis, solar energy is absorbed by the pigment called chlorophyll.
(d) During photosynthesis, plants take in Carbon dioxide and release Oxygen gas.
Q7. Name the following:
(i) A parasitic plant with yellow, slender and branched stem: Cuscuta
(ii) A plant that is partially autotrophic: Pitcher plant (An Insectivorous Plant)
(iii) The pores through which leaves exchange gases: Stomata
Q8. Tick the correct answer:
A8. Solution:
(a) Amarbel is an example of:
(i) Autotroph (ii) Parasite (iii) Saprotroph (iv) Host
(b) The plant which traps and feeds on insects is:
(a) Cuscuta (ii) China rose (iii) Pitcher plant (iv) Rose
Q9. Match the items given in Column I with those in Column II
A9. Solution:
Column- I Column-II
Chlorophyll -Leaf
Nitrogen -Rhizobium
Cuscuta- Parasite
Animals -Heterotrophs
Insects- Pitcher plant
Q10. 10. Mark ‘T’ if the statement is true and ‘F’ if it is false.
A 10. Solution:
(i) Carbon dioxide is released during photosynthesis. (F)
(ii) Plants which synthesize their food are called saprotrophs. (F)
(iii) The product of photosynthesis is not a protein. (T)
(iv) Solar energy is converted into chemical energy during photosynthesis. (T)
Q11. Choose the correct option from the following:
Which part of the plant takes in carbon dioxide from the air for photosynthesis?
(i) Root hair (ii) Stomata (iii) Leaf veins (iv) Petals
Solution: (iii) Stomata
Q12. Choose the correct option from the following:
Plants take carbon dioxide from the atmosphere mainly through their:
(i) roots (ii) stem (iii) flowers (iv) leaves
Solution: (iv) leaves
Q13. Why do farmers grow many fruits and vegetable crops inside large greenhouses? What are the advantages to the farmers?
A13. Fruits and vegetable crops are grown in large greenhouses because it protects crops from external climatic condition and to provide suitable temperature for the growth of crops. Advantages to farmers while growing fruits and vegetable crops inside greenhouses are
It protects crops from diseases and adverse climatic conditions.
It protects crops from wind and rodents





